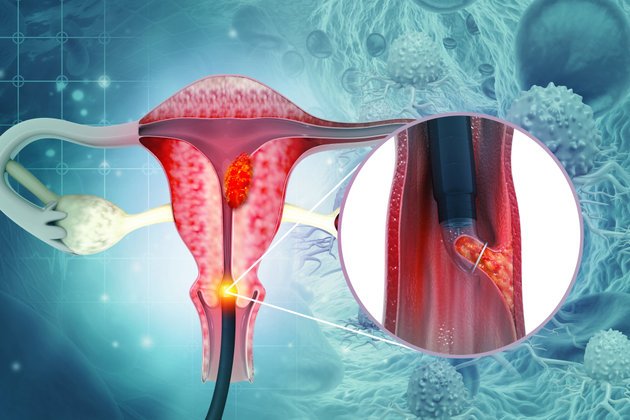
New Delhi, 10 January, 2026: Cervical Cancer Awareness Month serves as an important reminder to talk about Human Papillomavirus (HPV), the most common sexually transmitted infection worldwide and the leading cause of cervical cancer. What makes HPV particularly dangerous is that it often shows no clear symptoms for years, allowing the virus to silently damage cervical cells before a woman even realizes something is wrong.
Why HPV Often Goes Unnoticed?
HPV spreads mainly through skin-to-skin sexual contact and is so common that most sexually active people will contract it at some point in their lives. In many cases, the body’s immune system clears the infection on its own within one to two years. However, certain high-risk HPV types—especially HPV 16 and 18—can persist in the body and cause long-term changes in cervical cells, eventually leading to cervical cancer.
Because HPV rarely causes pain or visible signs in its early stages, many women remain unaware of the infection until abnormal cells are detected during routine screening or symptoms appear at an advanced stage.
Common HPV Infection Symptoms That May Be Missed
One of the most common signs of HPV is no symptom at all. This is why regular Pap smears and HPV testing are crucial. When symptoms do appear, they are often mild and easy to ignore.
Unusual vaginal discharge may occur in some cases. It can be watery, thick, or have a foul smell, but many women dismiss it as a minor infection or hormonal change.
Irregular vaginal bleeding is another subtle warning sign. Bleeding between periods, after sexual intercourse, or after menopause should never be ignored, as it may indicate cervical cell changes linked to persistent HPV infection.
Some women experience pelvic or lower back pain, especially during sexual intercourse. This discomfort may develop gradually and is often mistaken for menstrual cramps or urinary issues.
Genital warts, caused by low-risk HPV types, appear as small, flesh-colored or cauliflower-like bumps around the genital area. While these types usually do not cause cancer, their presence signals HPV exposure and increases the need for screening.
In advanced cases, women may notice fatigue, unexplained weight loss, or loss of appetite, symptoms that often appear when HPV-related cervical cancer has already progressed.
Why Early Detection Matters?
HPV-related cervical changes take years to turn into cancer, making early detection life-saving. A Pap smear can identify abnormal cervical cells long before cancer develops, while an HPV test can detect high-risk virus types even before cell changes begin.
Experts recommend that women who have been sexually active start regular screening in early adulthood and continue until at least 65 years of age. Early detection allows timely treatment, preventing cancer in most cases.
The HPV vaccine is a powerful tool in preventing cervical cancer. It protects against the most dangerous HPV strains and is most effective when given between the ages of 9 and 14, before sexual exposure. However, adults up to 45 years can still benefit from vaccination.
This Cervical Cancer Awareness Month, the message is clear: HPV may remain silent for years, but its consequences can be life-threatening. Regular screening, timely vaccination, and awareness of subtle symptoms can make the difference between early prevention and late diagnosis.












Leave a comment