Two more children died of suspected Chandipura virus infection in Gujarat on Tuesday, taking the total number of fatalities in the state to 8, Health Minister Rushikesh Patel said in a statement.
With this, the number of persons infected from the virus has gone up to 14, and eight of them have died, he told reporters in the state capital Gandhinagar.
According to the reports, all the cases have been reported from Sabarkantha, Aravalli, Mahisagar, Kheda, Mehsana and Rajkot districts.
On Monday, State’s Health Minister addressed the media, and said that the state health department has undertaken intensive surveillance of the affected districts, and special advisory has been issued to community and primary health centres and sub-district hospitals as well as medical colleges to treat suspected cases with certain symptoms as Chandipura virus cases.
“Mortality rate in the disease is high and it is difficult for a patient to survive if there is a delay in getting treatment,” he said.
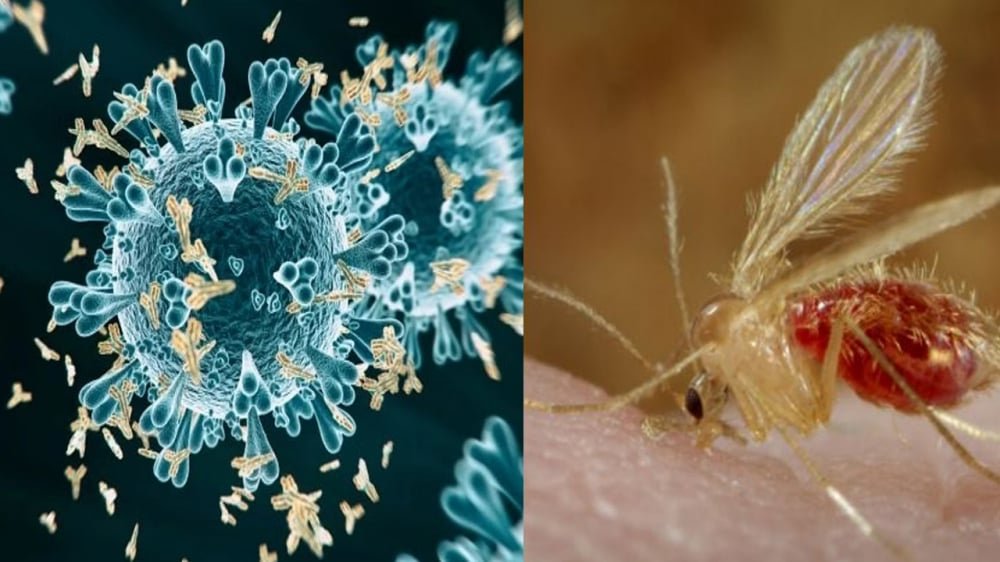
All You Need To Know About Chandipura Virus
The Chandipura virus, part of the Rhabdoviridae family, is highly contagious and primarily spread through sandflies’ bites. It poses a significant health threat in regions with these vectors. Discovered in Chandipura village, Maharashtra, India, the virus got its name from there.
Symptoms of Chandipura Virus
People infected with the Chandipura virus can show various symptoms including fever, headache, dizziness, muscle pain, and severe neurological issues like seizures and coma. Symptoms generally appear suddenly, with the virus being particularly dangerous for children and those with weakened immune systems.
How Does The Virus Transmits
The virus mainly spreads through bites from infected sandflies, especially the Phlebotomus species, which are most active at night and early morning. It can also spread through close contact with infected people or contaminated surfaces.
Prevention and Control Measures
To prevent Chandipura virus, several measures can be taken to reduce transmission risks. These include avoiding sandfly-infested areas, using insect repellents, wearing long-sleeved clothes, and maintaining proper sanitation to eliminate breeding sites. Research is ongoing for vaccines and antiviral treatments.
Chandipura Virus Infection: Treatment Options
Currently, there isn’t a specific antiviral treatment for the Chandipura virus. Treatment focuses on managing symptoms and complications, with hospitalization needed for severe cases, especially those involving neurological issues.












Leave a comment