A global initiative aimed at educating the public about uterine fibroids, which is a common but often overlooked women’s health condition. The focus this month is on empowering women with accurate information about the fibroid disease and the full spectrum of treatment options available to help lead a fibroid-free life.
What are Uterine Fibroids?
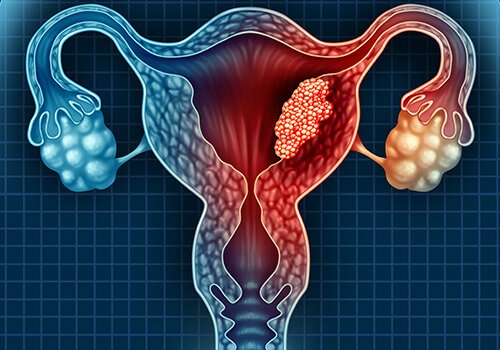
Uterine fibroids are benign, non-cancerous growths in the uterus that commonly occur in women of reproductive age. While many women experience no symptoms, others may face significant physical and emotional distress.
Symptoms include:
- Heavy menstrual bleeding, sometimes with clots
- Increase in menstrual cramps
- Periods lasting longer than usual
- Back or leg pain
- Abdominal swelling or protrusion
- Pressure-related symptoms like urination or bowel problems
- Pain during intercourse
- Fertility challenges, pregnancy and childbirth complications
In some cases, repeated heavy bleeding month after month can become dangerous, and may even require blood transfusion. Beyond physical health, these symptoms often impact a woman’s mental health, relationships, and professional life, compromising her overall quality of life.
What are the Treatment Options?
For years, surgical treatments like myomectomy (removal of fibroids) and hysterectomy (removal of the uterus) have considered the standard treatment options. While these still required in certain cases, less invasive options have emerged with evolving medical technology.
One such option is Uterine Fibroid Embolisation (UFE) – a minimally invasive, non-surgical procedure performed by interventional radiologists.
According to Dr. Basavaraj Biradar, Consultant Interventional Radiologist, Narayana Health, Mazumdar Shaw Medical Centre,
Bengaluru. Uterine fibroids, when symptomatic, usually have dilated uterine arteries that predominantly feed fibroids. An interventional radiologist accesses these uterine arteries through UFE.
A tiny incision is first made in the skin, usually in the femoral artery in the groin, and a thin tube known as the catheter inserted and guided into the uterine arteries using real-time imaging. Then, microscopic medical particles injected to block blood flow to the fibroids. This starves the fibroids of nutrients, causing them to shrink over time.
Women who decide to undergo the UFE procedure typically get back to work and their normal activities a week to 10 days after the procedure – a much shorter recovery time compared to conventional surgery.
Additional Advantages of UFE
- Treats multiple fibroids at once
- No scars or stitches on the abdomen
- No need for general anaesthesia
The American College of Obstetricians and Gynecologists (ACOG) hasrecognised UFE as a safe and effective alternative to hysterectomy for women with symptomatic fibroids who wish to retain their uterus. It best suited for women who have completed their families, as there limited data on long-term fertility outcomes.
Why Awareness Matters
Despite over 20 years of clinical use, UFE remains largely unknown among women. Many women suffer in silence, unaware that their symptoms could linked to fibroids. Some may embarrassed by the condition and unwilling to share their experiences with others. In addition, most do not have access to adequate information or treatment and thus may not know that less invasive treatments like UFE even exist.
Uterine Fibroid Awareness Month serves not only to raise awareness but also to encourage action. Women deserve access to comprehensive information that enables them to make informed decisions about their health.
At a time when medical advancements offer safer, quicker and less invasive treatments, not discussing all available options is a disservice to the public. Let this month be a reminder that awareness is the first step towards empowerment.












Leave a comment