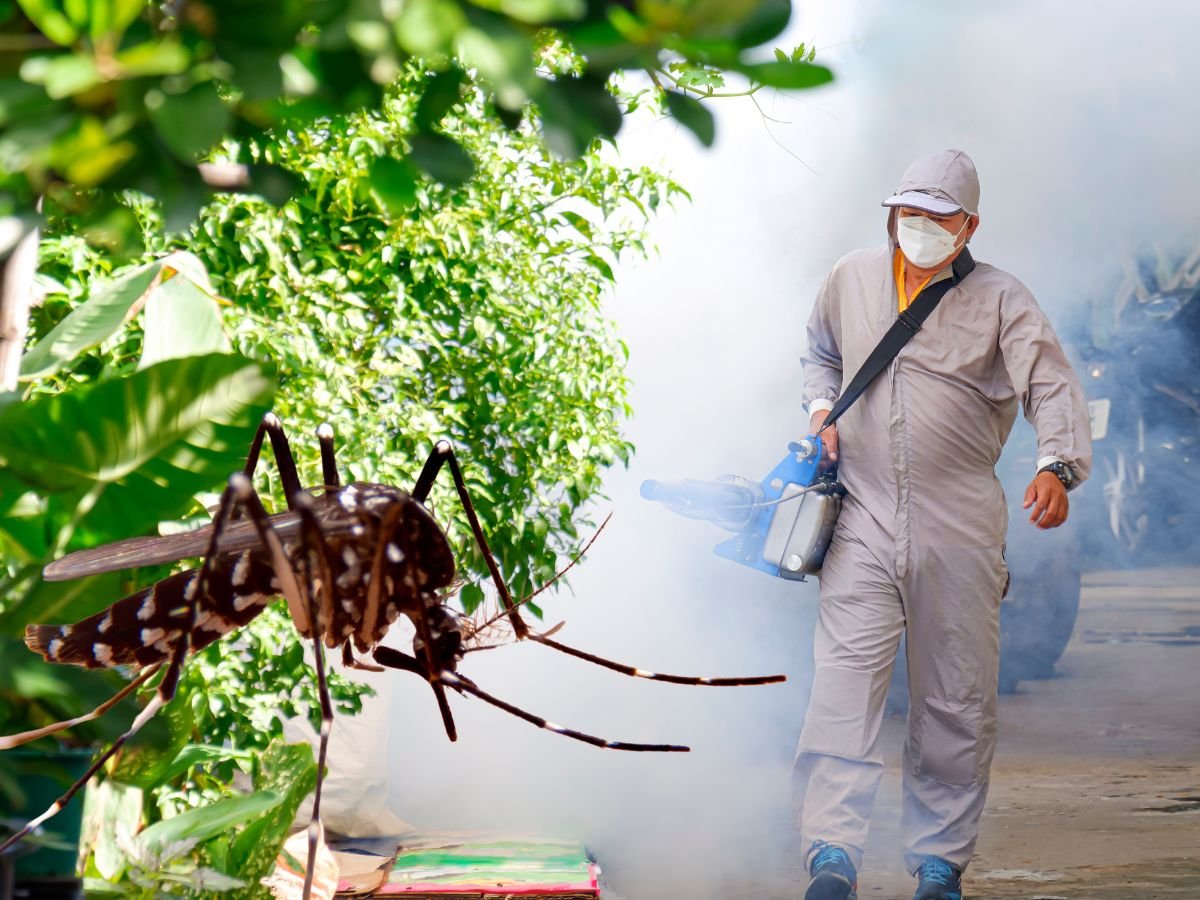
New Delhi, 30 August 2025: The United States has issued a Level 2 travel advisory for China following an explosive outbreak of chikungunya, a mosquito-borne viral disease spreading rapidly in parts of the country. Health officials have warned that thousands of people are at risk, and travelers are being urged to practice enhanced precautions when visiting affected areas, particularly Guangdong Province, where the outbreak is most severe.
The advisory has heightened global concern, as chikungunya has been steadily expanding in scope worldwide, with cases now reaching alarming levels in Asia and beyond.
The Scale of the Outbreak
China is currently witnessing one of its largest chikungunya outbreaks in recent history. The epicenter of the crisis has been identified in Foshan city, Guangdong Province, where local authorities are struggling to contain the surge in cases.
Reports indicate that over 7,000 infections have been recorded in China alone during this outbreak cycle. Globally, more than 240,000 people have been affected by chikungunya this year, with close to 90 deaths attributed to severe complications.
While chikungunya is rarely fatal, its ability to cause long-lasting and debilitating joint pain has made it a serious public health concern. Health experts caution that the real number of infections may be higher, as many cases go unreported or are misdiagnosed as dengue fever, which presents with similar symptoms.
What Is Chikungunya?
Chikungunya is a viral disease transmitted primarily by Aedes aegypti and Aedes albopictus mosquitoes—the same vectors responsible for spreading dengue and Zika. Unlike respiratory infections, chikungunya does not spread directly from person to person; transmission occurs only through the bite of infected mosquitoes.
Symptoms of the Disease
The illness usually begins with:
- Sudden high fever
- Severe joint and muscle pain
- Headache
- Skin rash
- Fatigue and weakness
Most patients recover within one to two weeks. However, in about 40% of cases, joint pain and swelling can persist for months or even years, affecting mobility and quality of life.
Although fatalities are rare, infants, the elderly, and individuals with pre-existing conditions such as diabetes or cardiovascular disease face higher risks of developing severe or life-threatening complications.
Why the Advisory Was Issued
The U.S. Centers for Disease Control and Prevention has classified travel to Guangdong under a Level 2 advisory: Practice Enhanced Precautions. This warning is a step below the highest alert but signals that conditions in the affected area pose significant health risks.
Authorities have urged travelers to remain vigilant, as mosquito activity in Guangdong remains exceptionally high due to humid weather and urban density.
The advisory also highlights the potential global spillover of the outbreak. International travel between China and other countries, including the United States, increases the risk of importing cases abroad. While the U.S. has not recorded locally transmitted cases since 2019, imported cases linked to travel have been steadily reported.
Safety Guidelines for Travelers
Health experts emphasize that there is no specific antiviral treatment for chikungunya. Supportive care, including rest, hydration, and pain relief medication, is the only form of therapy available.
Therefore, prevention is the best protection. Travelers heading to affected regions are advised to:
- Use insect repellents containing DEET, picaridin, or oil of lemon eucalyptus.
- Wear long-sleeved shirts and long pants to reduce skin exposure.
- Stay in air-conditioned or well-screened rooms, as mosquitoes breed in humid and stagnant conditions.
- Avoid mosquito hotspots, such as areas with standing water, especially during early morning and late afternoon when Aedes mosquitoes are most active.
- Get vaccinated if eligible, as chikungunya vaccines are now available in certain regions.
Pregnant women are being strongly advised to reconsider or postpone travel to outbreak zones due to the potential risk of transmitting the infection to newborns during or shortly after birth.
How China Is Responding
Authorities in China have rolled out aggressive containment measures in Guangdong Province. Large-scale mosquito control operations are underway, including aerial spraying, elimination of breeding grounds, and community-level cleanup drives to remove stagnant water.
Some cities have re-introduced strict public health protocols reminiscent of early COVID-19 response measures, including restrictions on outdoor gatherings and neighborhood-level monitoring to limit the spread of the disease.
Hospitals in Guangdong are also expanding capacity to handle the surge in patients presenting with fever and joint pain, while public awareness campaigns are educating residents on how to protect themselves from mosquito bites.
Global Context
The chikungunya outbreak in China is part of a broader trend of rising mosquito-borne diseases across the globe. Climate change, urbanization, and increased global travel have contributed to the spread of viruses like chikungunya, dengue, and Zika into new territories.
So far in 2025, chikungunya has been reported in dozens of countries, with particularly high numbers across Asia, Africa, and parts of South America. The rapid expansion of the disease has renewed calls for international cooperation on mosquito control strategies and vaccine development.
For the United States, imported cases remain a concern. Already this year, several dozen U.S. travelers returning from abroad have tested positive for chikungunya. While the risk of local outbreaks remains low for now, health authorities continue to monitor conditions closely.
What This Means for Travelers
For U.S. citizens and others planning to visit China, particularly Guangdong, the travel advisory underscores the importance of being proactive about health and safety.
Travelers should:
- Check the latest advisories before departure.
- Carry adequate supplies of mosquito repellent and protective clothing.
- Seek medical attention immediately if they develop fever, rash, or joint pain during or after their trip.
Health officials also recommend registering with local embassies or consulates during travel, which allows for quick communication in case the outbreak worsens or travel restrictions are implemented.
The U.S. travel advisory for China over the chikungunya outbreak marks a significant moment in global public health vigilance. With thousands of cases already reported and risks continuing to rise, the situation highlights the growing threat of mosquito-borne diseases in a warming, interconnected world.
For now, prevention remains the most effective tool against chikungunya. Travelers are being urged to take enhanced precautions to protect themselves, while governments continue working to contain the outbreak and prevent it from spreading further across borders.
The coming weeks will be critical in determining whether the outbreak stabilizes or escalates further. Until then, travelers to Guangdong and surrounding regions are advised to remain cautious, vigilant, and well-prepared.














Leave a comment