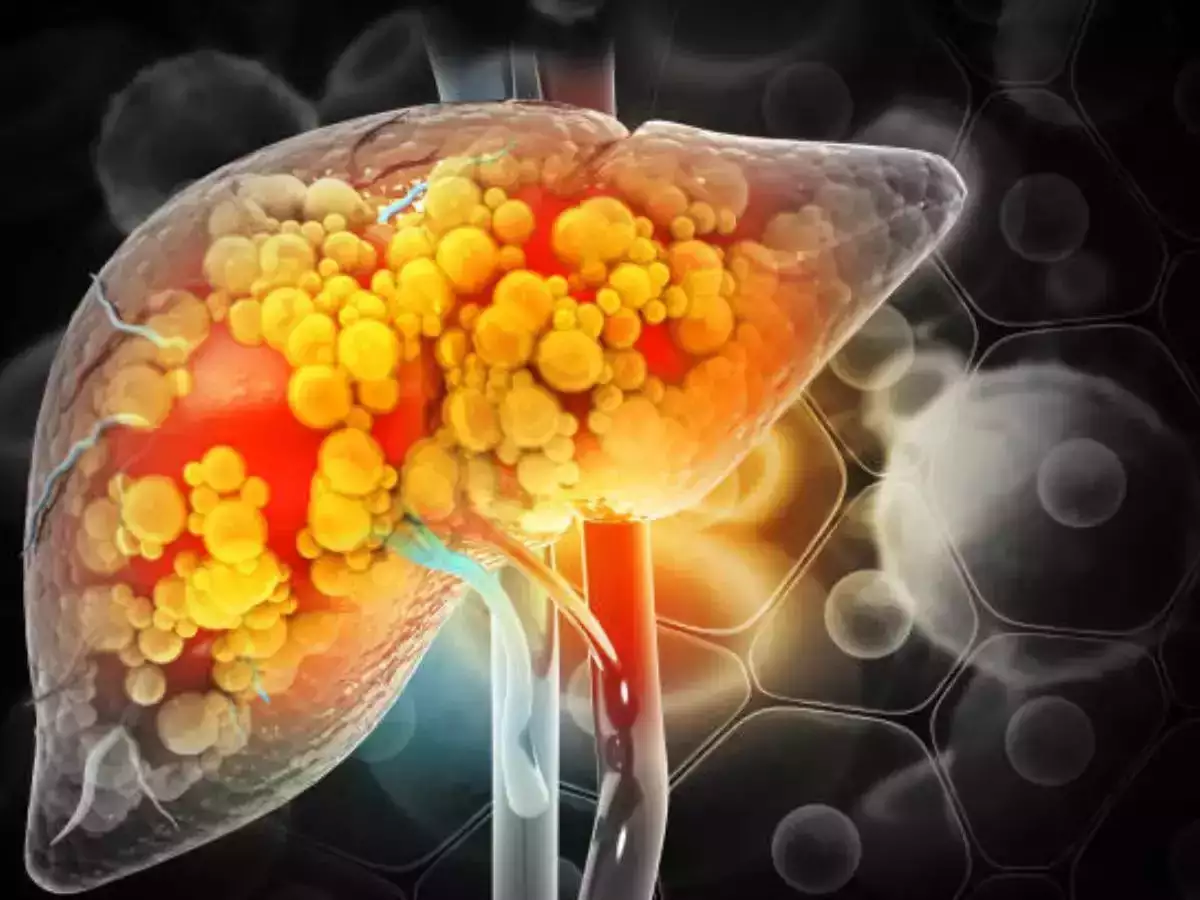
New Delhi, 25 May 2025: Fatty liver disease, once considered an adult health issue, is now increasingly prevalent among children and adolescents. This condition, characterized by the accumulation of fat in liver cells, can lead to serious health complications if left unaddressed. Dr. Neelam Mohan, a renowned pediatric hepatologist and gastroenterologist, emphasizes the urgency of early detection and intervention to prevent long-term liver damage in young patients.
Understanding Fatty Liver Disease in Children
Fatty liver disease in children, medically referred to as non-alcoholic fatty liver disease (NAFLD), encompasses a spectrum of liver conditions ranging from simple fat accumulation (steatosis) to non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), which involves inflammation and can progress to cirrhosis or liver failure. Dr. Mohan notes that with the rise in childhood obesity and sedentary lifestyles, NAFLD has become the most common chronic liver disease in the pediatric population.
Causes and Risk Factors
Several factors contribute to the development of fatty liver disease in children:
- Obesity: Excess body weight, particularly central obesity, is a significant risk factor.
- Insulin Resistance: Conditions like prediabetes and type 2 diabetes increase susceptibility.
- High Cholesterol and Triglycerides: Elevated lipid levels can exacerbate fat accumulation in the liver.
- Genetic Predisposition: A family history of liver disease may increase risk.
- Poor Diet: High intake of added sugars and saturated fats contributes to liver fat deposition.
Dr. Mohan highlights that the liver is involved in 10-20% of obese children, with the severity of liver involvement increasing with the degree of obesity.
Symptoms to Watch For
Fatty liver disease is often asymptomatic in its early stages, making it challenging to diagnose without medical testing. However, some children may exhibit:
- Persistent fatigue
- Abdominal discomfort, especially in the upper right quadrant
- Unexplained weight gain
- Elevated liver enzymes detected through blood tests
In advanced cases, symptoms may progress to jaundice, swelling, and signs of liver dysfunction.
How to stay safe? Dr. Mohan emphasizes the importance of a multidisciplinary approach involving dietitians, physical therapists, and pediatricians to support children and their families in making sustainable lifestyle changes.
Expert Insight: Dr. Neelam Mohan
Dr. Neelam Mohan is a distinguished pediatric hepatologist and gastroenterologist with over 25 years of experience. She has been instrumental in establishing India’s first pediatric liver transplant program and has contributed significantly to the development of national and international guidelines for managing pediatric liver diseases, including fatty liver disease.
Her expertise underscores the critical need for awareness, early detection, and comprehensive management of fatty liver disease in children to ensure better health outcomes.
Fatty liver disease in children is a growing public health concern that necessitates prompt attention and action. By understanding the risk factors, recognizing early symptoms, and implementing preventive measures, parents and healthcare providers can work together to combat this silent epidemic. With guidance from experts like Dr. Neelam Mohan, we can strive towards a future where children are safeguarded against the long-term consequences of liver disease.












Leave a comment