New Delhi, 27 November, 2025: As the temperatures drop and winter sets in, the body faces unique challenges. Cold weather doesn’t just mean bundling up—it directly affects the heart, joints, and lungs, increasing the risk of health complications. For many, winter can bring joint stiffness, respiratory issues, and even heightened cardiovascular risk. Understanding these seasonal effects and adopting preventive strategies can help you stay healthy, comfortable, and active all winter long.
The Winter Effect on the Heart
Cold weather is a well-known trigger for cardiovascular stress. Here’s why:
1. Vasoconstriction and Blood Pressure
In cold conditions, blood vessels constrict to preserve body heat. This increases blood pressure and workload on the heart, putting extra strain on individuals with hypertension or pre-existing heart conditions.
2. Higher Risk of Heart Attacks
Studies show that heart attacks and strokes peak during winter months. The combination of cold temperatures, reduced physical activity, and seasonal infections can trigger acute cardiovascular events.
3. Impact of Respiratory Infections
Winter brings a rise in flu and respiratory infections, which can increase heart strain and exacerbate chronic heart conditions.
4. Tips to Protect Your Heart
- Stay warm: Dress in layers, cover extremities, and avoid sudden exposure to cold.
- Maintain activity: Light exercise indoors can improve circulation and reduce risk.
- Monitor blood pressure: Keep track of levels and follow medication guidance.
- Vaccinations: Flu and pneumonia vaccines help reduce infection-related cardiac stress.
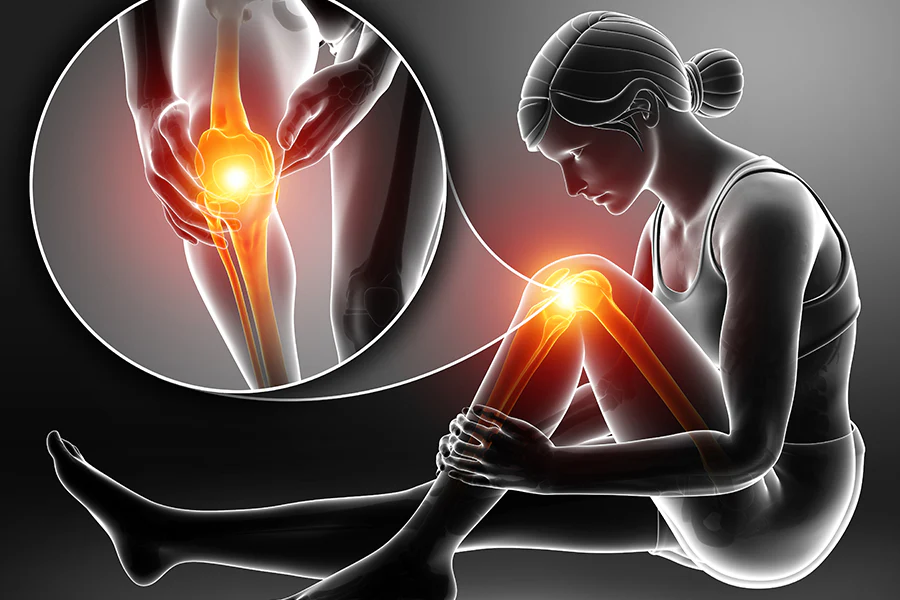
How Winter Affects the Joints
Cold weather often worsens joint pain and stiffness, particularly in people with arthritis or joint injuries.
1. Reduced Synovial Fluid and Lubrication
Colder temperatures can slow the flow of synovial fluid, the lubricant that helps joints move smoothly, leading to stiffness.
2. Changes in Barometric Pressure
Some people are sensitive to drops in barometric pressure, which can increase pain in arthritic or previously injured joints.
3. Muscle Tightness
Cold muscles are less flexible, which can:
- Increase stiffness
- Reduce range of motion
- Heighten the risk of injury
4. Tips for Joint Health in Winter
- Stay active indoors: Yoga, stretching, or light resistance training keeps joints mobile.
- Keep warm: Thermal clothing, heated blankets, and warm baths help maintain joint comfort.
- Supportive supplements: Consult a healthcare provider about vitamin D, calcium, or joint-supporting nutrients.
- Pain management: Over-the-counter anti-inflammatory medications may be used under professional guidance.
The Lungs and Winter Air
Cold weather can be tough on the respiratory system, affecting both healthy individuals and those with lung conditions.
1. Cold Air Irritation
Breathing cold, dry air can:
- Trigger bronchospasms in asthmatics
- Cause coughing or shortness of breath
- Irritate the airways in susceptible individuals
2. Increased Risk of Respiratory Infections
Indoor heating and crowded environments in winter facilitate the spread of influenza, common cold, and pneumonia, which can challenge lung function.
3. Tips for Healthy Lungs
- Wear scarves or masks: Cover your mouth and nose to warm and humidify the air before inhaling.
- Use humidifiers: Maintaining indoor humidity helps prevent airway dryness.
- Vaccinations: Annual flu shots and pneumonia vaccines reduce infection risks.
- Practice breathing exercises: Gentle breathing techniques can improve lung capacity and reduce sensitivity to cold air.
Nutrition for Winter Wellness
A well-balanced diet is essential to support heart, joint, and lung health during colder months.
1. Heart Health
- Increase intake of omega-3 fatty acids from fish, flaxseeds, or walnuts.
- Reduce saturated fats, processed foods, and excess salt.
- Include fiber-rich foods like oats, legumes, and vegetables.
2. Joint Health
- Anti-inflammatory foods help reduce stiffness and pain:
- Fatty fish (salmon, mackerel)
- Turmeric and ginger
- Leafy greens
- Adequate vitamin D and calcium strengthen bones.
3. Lung Support
- Foods rich in antioxidants and vitamin C improve immunity:
- Citrus fruits, berries, and bell peppers
- Hydration is crucial to keep airways moist and clear.
Lifestyle Adjustments for Winter Health
1. Exercise Indoors
Regular physical activity is crucial:
- Reduces stiffness and improves circulation
- Boosts heart and lung function
- Supports mood and energy levels
Options include yoga, pilates, resistance bands, stationary cycling, or brisk walking indoors.
2. Layer Clothing Wisely
Proper layering keeps core temperature stable and protects extremities. Consider moisture-wicking layers and insulated outerwear for outdoor activity.
3. Monitor Indoor Air Quality
- Avoid overly dry indoor air with humidifiers
- Ensure proper ventilation
- Reduce exposure to pollutants and smoke
4. Stress Management
Winter months can contribute to seasonal affective disorder (SAD) or increased stress, which may indirectly affect heart and joint health. Strategies include:
- Meditation or mindfulness
- Light exposure therapy
- Staying socially connected
When to Seek Medical Attention
Pay attention to warning signs that may indicate serious issues during winter:
Heart-related symptoms:
- Chest pain or tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Lightheadedness or sudden fatigue
Joint issues:
- Sudden swelling or severe pain
- Reduced mobility or redness around joints
Respiratory concerns:
- Persistent cough
- Wheezing or difficulty breathing
- Fever or signs of infection
Early intervention can prevent complications and improve outcomes.
Seasonal Vaccinations
Winter is the perfect time to update vaccines, which protect against infections that stress the heart, joints, and lungs:
- Influenza vaccine – Reduces flu risk and related complications
- Pneumococcal vaccine – Protects against pneumonia, particularly in older adults and high-risk populations
- COVID-19 booster shots – Important for maintaining immunity against severe illness
Vaccinations are a simple yet highly effective tool in winter wellness.
Maintaining Routine Health Checks
Winter often brings busy schedules and holidays, but regular check-ups remain crucial:
- Blood pressure and cholesterol monitoring
- Diabetes management
- Joint assessments for arthritis or pain
- Pulmonary function tests for chronic lung conditions
Preventive care ensures that seasonal stressors don’t exacerbate underlying health problems.
Mental and Emotional Wellness
Winter affects mental health, which in turn impacts physical wellness:
- Seasonal affective disorder (SAD) can lead to fatigue and low motivation
- Stress and isolation may worsen heart and joint health
- Maintaining routines, staying active, and light exposure are key strategies
Holistic winter wellness includes mind-body balance, not just physical protection.
Winter may pose challenges, but with proactive measures, you can safeguard your heart, joints, and lungs. Key strategies include:
- Dressing appropriately for cold temperatures
- Staying active and maintaining flexibility
- Eating a nutrient-rich diet
- Keeping indoor air clean and humidified
- Staying up to date with vaccinations
- Monitoring health and seeking medical care promptly
By approaching winter with a holistic, informed plan, you can enjoy the season without compromising your health. Winter wellness isn’t just surviving—it’s thriving, even in the coldest months.