Chronic stress has a profound and often underestimated impact on the immune system, influencing the body’s ability to fight infections, heal wounds, and maintain overall health, and understanding this connection is essential for anyone looking to strengthen their natural defenses, as prolonged exposure to stress triggers the release of cortisol and other stress hormones that suppress immune cell function, reduce the production of protective antibodies, and increase inflammation, making the body more susceptible to illnesses ranging from the common cold to more serious infections, while also slowing recovery times and exacerbating chronic health conditions; additionally, stress disrupts sleep patterns, which further impairs immune responses because restorative sleep is essential for the production of cytokines and other immune-regulating compounds, meaning that individuals under constant stress may find themselves not only more prone to infections but also experiencing delayed healing and heightened inflammatory responses that contribute to long-term disease risk.
Stress also influences lifestyle behaviors that indirectly weaken immunity, as it can lead to poor dietary choices, increased consumption of processed foods, decreased physical activity, excessive alcohol intake, and smoking, all of which negatively affect the body’s defense mechanisms, while simultaneously increasing susceptibility to autoimmune and inflammatory disorders.
Psychological stress can also compromise the gut microbiome, which plays a critical role in immune function, as alterations in gut bacteria due to stress can reduce the production of protective metabolites, disrupt the balance of immune cells, and make the gastrointestinal system more vulnerable to infections, further highlighting the interconnectedness of mental and physical health. Hormonal imbalances caused by chronic stress can impair the function of lymphocytes, natural killer cells, and other critical immune components, while simultaneously promoting chronic low-grade inflammation, which has been linked to cardiovascular disease, diabetes, and other chronic conditions, underscoring the importance of managing stress to protect long-term health.
To mitigate the negative effects of stress on immunity, experts recommend adopting evidence-based strategies such as mindfulness meditation, deep breathing exercises, progressive muscle relaxation, and yoga, which help reduce cortisol levels and improve immune cell function, while also promoting mental clarity and emotional resilience.
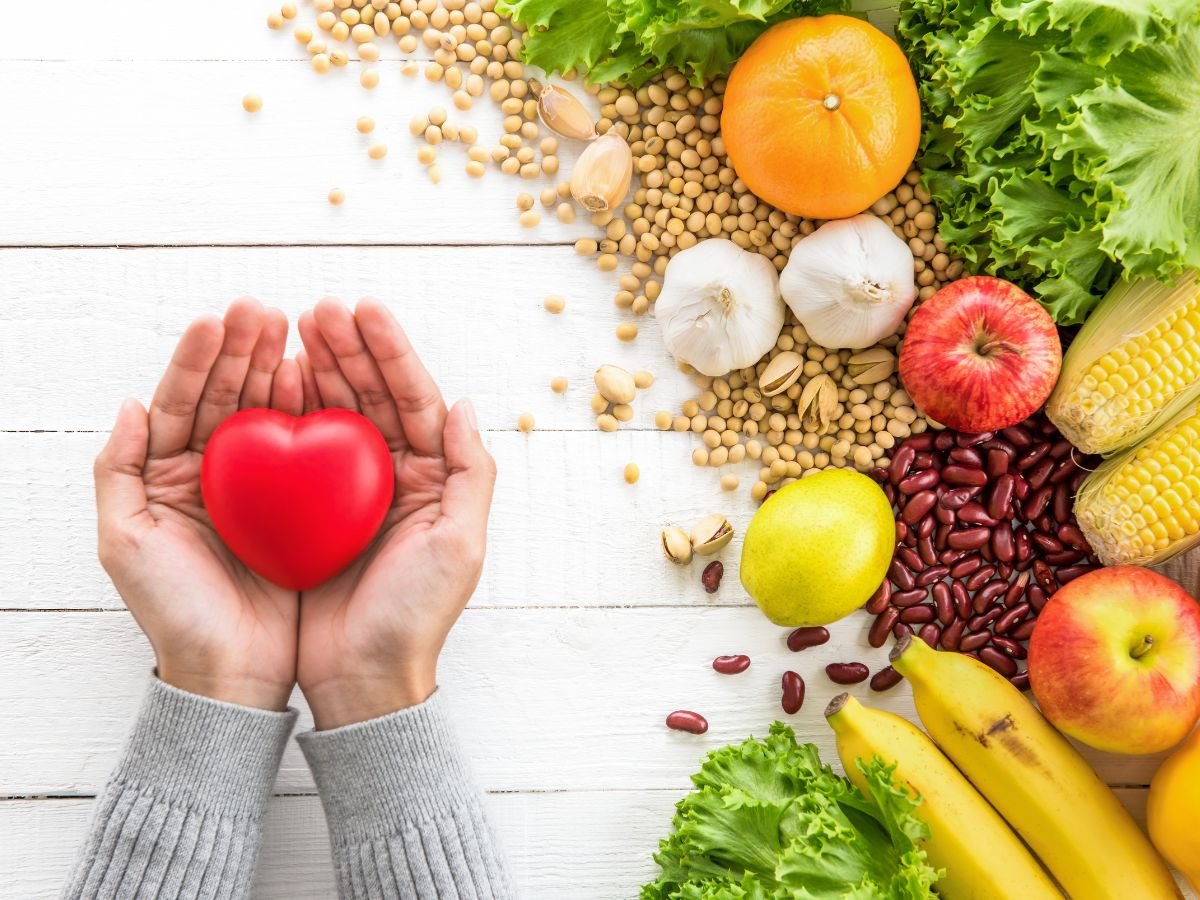
Regular physical activity is another effective approach, as moderate exercise enhances circulation, facilitates the efficient transport of immune cells throughout the body, and reduces stress hormone levels, whereas excessive or intense exercise without recovery can exacerbate stress and temporarily suppress immunity. Nutrition also plays a vital role in supporting the immune system under stress, with a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats providing essential vitamins and minerals, such as vitamin C, vitamin D, zinc, and antioxidants, which help maintain optimal immune function and counteract inflammation induced by stress.
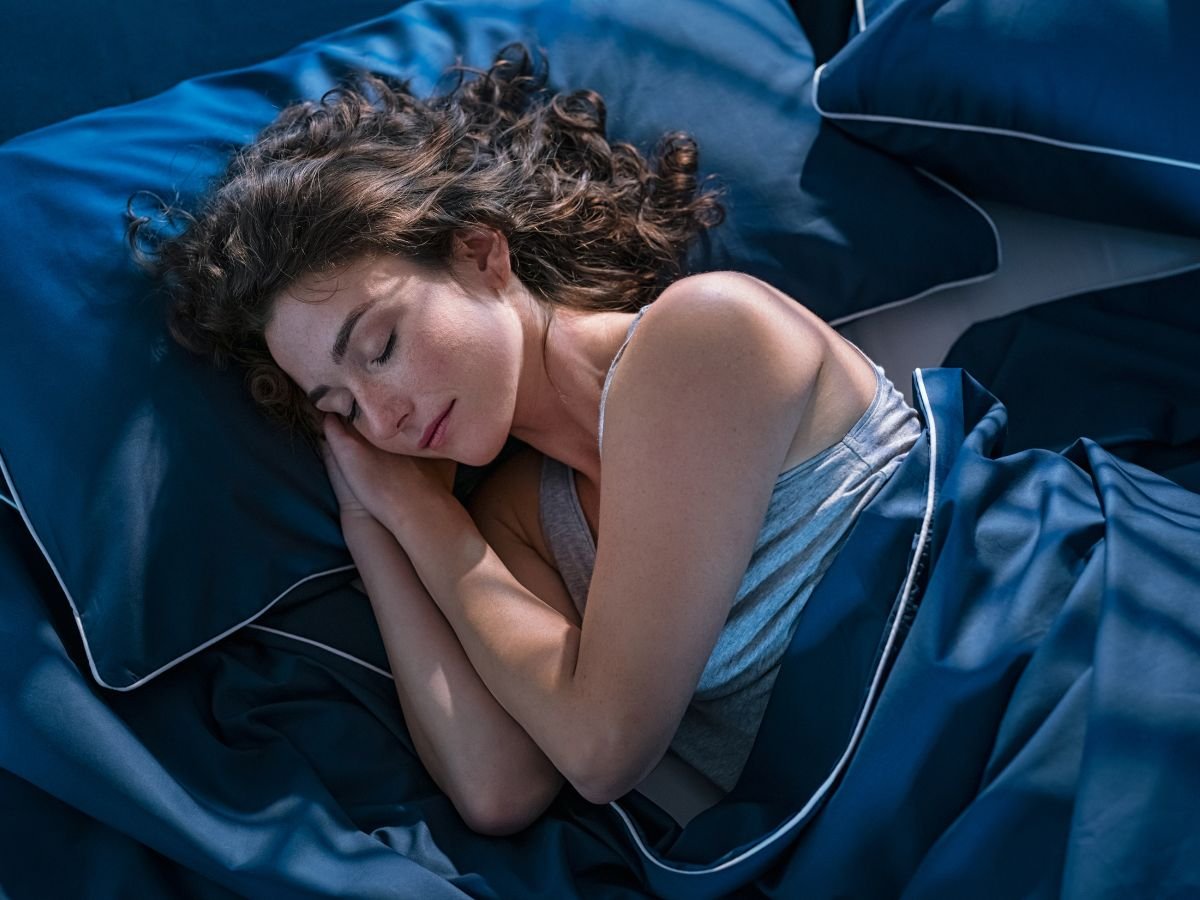
Adequate sleep is equally important, as it allows the immune system to repair, regenerate, and produce protective cytokines, so maintaining a consistent sleep schedule and practicing good sleep hygiene can help buffer the negative impact of stress on immunity. Social support and positive interpersonal relationships have also been shown to strengthen immune responses, reduce perceived stress, and improve overall well-being, emphasizing the importance of emotional health in maintaining physical health. Incorporating these strategies into daily routines, along with regular medical checkups and monitoring of stress-related symptoms, can help individuals maintain a robust immune system despite the unavoidable stressors of modern life.
Recognizing the powerful link between stress and immunity is critical, as unmanaged stress not only increases vulnerability to infections and illnesses but also accelerates aging, exacerbates inflammation, and contributes to chronic disease development; by prioritizing stress management, balanced nutrition, physical activity, sufficient sleep, and social support, individuals can protect their immune system, enhance overall resilience, and improve both physical and mental health outcomes, demonstrating that controlling stress is a foundational aspect of preventive health and long-term wellness.












Leave a comment