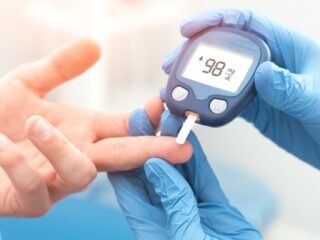
New Delhi, 26 November, 2025: Diabetes is a chronic condition that affects millions of people worldwide. Often called a “silent disease,” it can develop gradually and remain undiagnosed for years. Early detection is crucial to prevent complications such as heart disease, kidney problems, nerve damage, and vision loss. Knowing the early warning signs can make a significant difference in timely diagnosis and effective management.
Here are the 10 early warning signs of diabetes that everyone should recognize.
1. Excessive Thirst (Polydipsia)
One of the most common early signs of diabetes is unusual thirst. When blood sugar levels are high, your kidneys work harder to filter and absorb the excess glucose. This process draws fluid from tissues, making you feel dehydrated and prompting frequent drinking.
- Drinking water constantly yet still feeling thirsty
- Dry mouth or a persistent sense of thirst
Excessive thirst can indicate that your blood sugar is out of balance and should not be ignored.
2. Frequent Urination (Polyuria)
Along with thirst, frequent urination is another early warning sign. The kidneys attempt to rid the body of extra sugar through urine, leading to:
- Needing to urinate more often, especially at night
- Increased volume of urine
If you notice a sudden change in urination patterns, it’s essential to get your blood sugar checked.
3. Unexplained Weight Loss
Unexpected weight loss, despite normal or increased eating, can signal diabetes. When the body cannot properly use glucose for energy, it starts breaking down muscle and fat for fuel, resulting in weight loss.
- Rapid weight loss over a short period
- Loss of muscle tone and strength
This symptom is common in type 1 diabetes but can also occur in type 2.
4. Extreme Hunger (Polyphagia)
Even when eating regularly, people with diabetes may experience persistent hunger. This occurs because cells cannot absorb glucose efficiently, leaving the body feeling energy-deprived.
- Eating frequently without feeling satisfied
- Cravings for sugary or high-carb foods
This symptom often accompanies fatigue and unexplained weight loss.
5. Fatigue
Feeling unusually tired is a common symptom of early diabetes. When glucose cannot enter cells, your body lacks energy.
- Persistent tiredness even after adequate sleep
- Difficulty concentrating or performing daily tasks
Chronic fatigue may indicate that blood sugar levels are elevated or fluctuating.
6. Blurred Vision
High blood sugar can cause the lens of the eye to swell, affecting your focus. This leads to blurred or fluctuating vision, sometimes noticed early in diabetes.
- Difficulty seeing clearly at near or far distances
- Vision changes that appear suddenly or intermittently
If left untreated, diabetes can lead to diabetic retinopathy, a serious eye condition that can cause vision loss.
7. Slow-Healing Wounds
Diabetes can impair your body’s ability to heal wounds due to poor blood circulation and high blood sugar. Early signs include:
- Cuts and bruises that take longer than usual to heal
- Sores or infections on the skin that persist
Prompt attention to slow-healing wounds is critical to prevent complications like infections or ulcers.
8. Tingling or Numbness in Hands and Feet (Neuropathy)
High blood sugar can damage nerves, causing diabetic neuropathy. Early symptoms include:
- Tingling or “pins and needles” sensation in fingers or toes
- Numbness or burning pain in extremities
- Reduced sensitivity to touch or temperature
Detecting neuropathy early allows for interventions that can prevent permanent nerve damage.
9. Dark Patches on Skin (Acanthosis Nigricans)
Some people with diabetes develop dark, velvety patches on areas like the neck, armpits, or groin. This condition, known as acanthosis nigricans, is often associated with insulin resistance, a precursor to type 2 diabetes.
- Thickened, darkened skin
- Itchiness or discomfort in affected areas
This physical sign can be an early indicator that your body is struggling with blood sugar regulation.
10. Frequent Infections
High blood sugar weakens the immune system, making you more prone to infections. People with undiagnosed diabetes may experience:
- Recurrent urinary tract infections (UTIs)
- Skin infections, fungal infections, or gum problems
- Persistent inflammation or slow recovery from illness
Frequent infections should prompt a discussion with a healthcare provider about possible blood sugar issues.
Why Early Detection Matters
Early recognition of diabetes symptoms allows for timely intervention, which can prevent or delay serious complications, including:
- Heart disease and stroke
- Kidney damage (diabetic nephropathy)
- Nerve damage (neuropathy)
- Vision problems (diabetic retinopathy)
- Foot ulcers and infections
Lifestyle modifications, medication, and regular monitoring can effectively manage diabetes and reduce long-term risks.
Who Is at Risk?
While diabetes can affect anyone, certain factors increase susceptibility:
- Family history of diabetes
- Being overweight or obese
- Sedentary lifestyle
- Age over 40
- History of gestational diabetes or polycystic ovary syndrome (PCOS)
- High blood pressure or cholesterol
Even individuals without these risk factors should be aware of the early warning signs.
Steps to Take If You Notice Symptoms
- Schedule a blood sugar test: A simple fasting glucose test or HbA1c test can determine your blood sugar levels.
- Consult a healthcare professional: Early diagnosis helps prevent complications.
- Adopt a healthy lifestyle: Regular exercise, balanced diet, and weight management improve blood sugar control.
- Follow medical advice: If diagnosed, medications or insulin therapy may be necessary.
- Monitor your health regularly: Routine checks ensure your blood sugar remains in a safe range.
Lifestyle Tips for Prevention
Even if you’re not diabetic, certain lifestyle choices can reduce your risk:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Engage in at least 30 minutes of daily physical activity
- Eat a balanced diet rich in vegetables, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats
- Limit sugary foods and refined carbohydrates
- Avoid smoking and excessive alcohol consumption
- Manage stress and ensure adequate sleep
Preventive measures can dramatically reduce your risk of developing type 2 diabetes.
Diabetes often develops silently, but your body sends subtle signals before the disease becomes severe. Excessive thirst, frequent urination, unexplained weight loss, fatigue, blurred vision, slow-healing wounds, numbness, dark skin patches, and frequent infections are all early warning signs that should not be ignored.
Recognizing these symptoms and taking prompt action can prevent complications, improve quality of life, and support long-term health. By staying vigilant, maintaining a healthy lifestyle, and seeking medical advice when needed, you can take control of your health and reduce the impact of diabetes on your life.