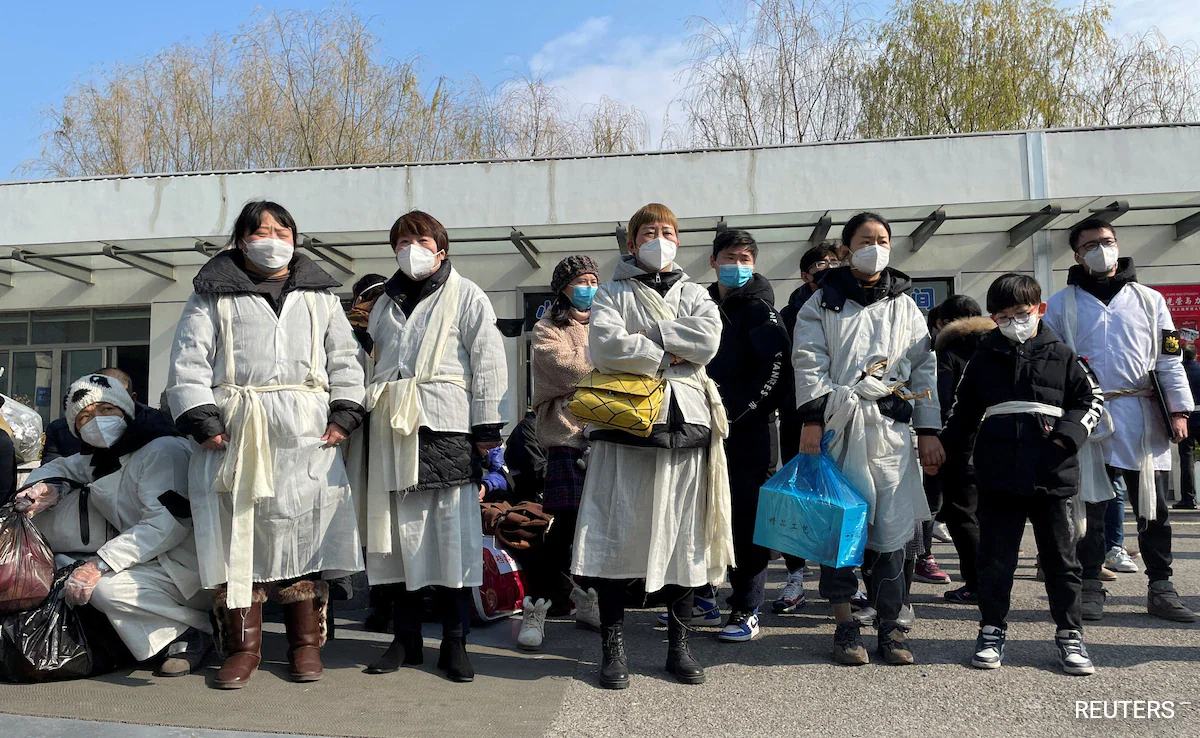
New Delhi, 13 January 2025: Health officials in Northern China have reported a decline in cases of the Human Metapneumovirus (HMPV), offering a glimmer of hope amid rising global concerns. The virus, which primarily causes respiratory infections, has triggered international alarm due to its increasing prevalence and severity, particularly among vulnerable populations such as children and the elderly.
Recent Trends in Northern China
Reports indicate that Northern China has seen a steady decrease in HMPV cases over the past few weeks. Public health experts credit this decline to intensified awareness campaigns, improved hygiene practices, and the timely isolation of infected individuals. Despite this positive trend, health officials urge vigilance, emphasizing that the virus remains a global threat.
HMPV: A Global Health Concern
HMPV has been linked to symptoms such as fever, cough, and difficulty breathing, which can escalate to pneumonia in severe cases. The virus spreads through respiratory droplets, much like the flu, making it a highly transmissible pathogen. Countries worldwide have reported an uptick in cases, raising concerns about its potential to overwhelm healthcare systems.
Preventive Measures Taken in China
Northern China has implemented robust measures to control the spread of HMPV. These include:
Public Awareness Drives: Educating communities about the symptoms and transmission of HMPV.
Enhanced Surveillance: Monitoring cases to detect outbreaks early.
Hospital Preparedness: Equipping medical facilities to handle severe cases effectively.
Global Implications
The decline in HMPV cases in Northern China is encouraging, but experts warn that the virus could resurge, particularly in regions with less stringent public health measures. The World Health Organization (WHO) has advised nations to prioritize research and resource allocation to prevent further outbreaks.
While the situation in Northern China brings cautious optimism, the global community must remain proactive in tackling HMPV. Continued vigilance, public health initiatives, and international collaboration will be critical to mitigating the threat posed by this virus.