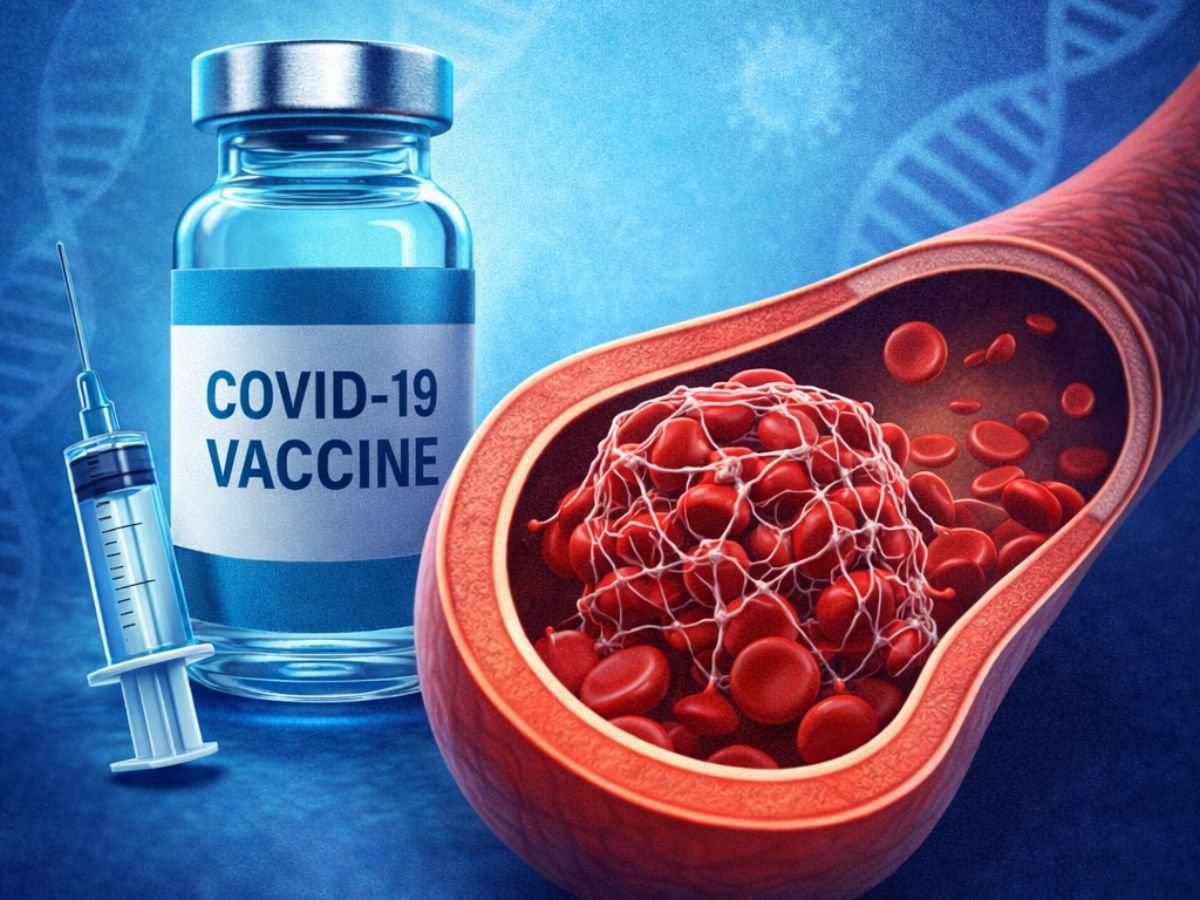
During the global rollout of COVID-19 vaccines, millions of lives were saved, severe illness was prevented, and hospitals around the world were relieved from being overwhelmed. Yet amid the massive vaccination campaigns, a puzzling phenomenon appeared: a very small number of people developed rare but serious blood clots after receiving certain COVID-19 vaccines. This triggered widespread concern and intense scientific investigation, as experts sought to understand the cause of these unexpected events.
Years after the first reports emerged, scientists have now pinpointed the biological mechanism behind these rare clotting events. The discovery brings clarity to a public health mystery and provides important insights for safer vaccine development in the future.
The Emergence of Rare Blood Clots
In early 2021, reports surfaced from several countries that some individuals were developing unusual clots, sometimes life-threatening, after receiving COVID-19 vaccines. These cases were typically paired with low platelet counts, a paradoxical combination of clotting and bleeding. The condition was later named Vaccine-Induced Immune Thrombotic Thrombocytopenia (VITT), or sometimes Thrombosis with Thrombocytopenia Syndrome (TTS).
These events were most commonly reported after vaccines that used a viral vector platform, specifically adenovirus-based vaccines such as AstraZeneca (known as Covishield in some countries) and Johnson & Johnson’s Janssen vaccine. Despite the rarity of these incidents, the severity and unique characteristics of the clotting events drew immediate attention from public health authorities and scientists alike.
Although these adverse events were extremely uncommon—occurring in approximately 1 in 200,000 individuals—their serious nature, often involving cerebral venous sinus thrombosis (clots in brain veins) or abdominal clots, required urgent investigation.
Early Clues from the Immune System
Researchers initially discovered that affected individuals produced antibodies against Platelet Factor 4 (PF4), a protein naturally present in the blood that regulates clotting. Normally, PF4 functions safely within the clotting process, but when antibodies bind to it abnormally, they can trigger the activation of platelets and formation of blood clots.
The condition resembled a rare side effect called heparin-induced thrombocytopenia (HIT), which occurs in some patients receiving the blood thinner heparin. However, VITT was distinct because patients had never been exposed to heparin, indicating a unique immune reaction.
Patients presented with clots in uncommon locations and low platelet counts, which differed from typical clotting disorders. This suggested that the body’s immune system had been inadvertently triggered to create a dangerous chain reaction.
The Breakthrough Discovery
In early 2026, researchers published findings that definitively explained the underlying cause of VITT. Using advanced molecular and genetic analysis, scientists demonstrated that the rare clotting events were caused by a specific mutation in antibodies produced by certain individuals.
Here is what they uncovered:
1. The Role of Adenovirus Vectors
Adenoviruses serve as vehicles for delivering SARS-CoV-2 genetic material into human cells. For most people, this process is harmless and triggers a protective immune response. However, in rare cases, interactions between the adenovirus vector and the immune system caused an abnormal antibody response in susceptible individuals.
2. Mutated Antibodies Bind to PF4
The researchers discovered that individuals affected by VITT produced antibodies with a specific mutation. This mutation caused the antibodies to bind tightly to PF4, forming immune complexes. Once these complexes formed, they activated platelets, which in turn triggered clot formation, despite low platelet counts elsewhere in the bloodstream.
This explained the unusual paradox of simultaneous clotting and thrombocytopenia. Notably, the same antibody mutation was observed across multiple patients worldwide, highlighting a clear pattern.
3. Clotting Cascade
The binding of these mutated antibodies to PF4 initiated a cascade of platelet activation. Once platelets were activated, they aggregated and initiated clot formation. This chain reaction resulted in rare but dangerous clots, often appearing in unusual locations such as the brain or abdomen.
This mechanism confirmed that the condition was immune-mediated, not a direct effect of the virus spike protein or vaccine ingredient itself.
Clinical Implications and Treatment
The identification of the precise mechanism has significant implications for both vaccine safety and clinical treatment. Clinicians now understand that VITT requires a distinct approach to treatment compared to standard blood clots. Traditional anticoagulants like heparin may worsen the condition, while non-heparin-based therapies are preferred.
Early detection remains crucial. Symptoms typically appear 4 to 42 days after vaccination and may include:
- Severe headaches or blurred vision
- Abdominal pain
- Leg swelling or pain
- Shortness of breath
- Unusual bruising or bleeding
Prompt recognition and treatment dramatically improve outcomes. Public health authorities continue to emphasize that the benefits of COVID-19 vaccination far outweigh the extremely rare risk of VITT.
The Rarity and Safety Context
While these clotting events captured headlines, they remain extremely uncommon. Data from millions of vaccinated individuals indicate that only a tiny fraction experienced VITT, reinforcing that COVID vaccines are overwhelmingly safe for the general population.
Regulatory agencies such as the European Medicines Agency (EMA) and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) have reviewed extensive data and reaffirmed vaccine safety, while providing clear guidance on risk recognition and management.
Broader Implications for Vaccine Design
Understanding the precise cause of VITT provides critical insights for the development of safer vaccines in the future. Scientists can now:
- Design adenovirus vectors that minimize unintended immune activation
- Develop diagnostic tools to identify individuals potentially at risk
- Guide clinicians in personalized treatment approaches for rare adverse events
The discovery highlights the importance of robust global surveillance and scientific investigation, demonstrating that even rare side effects can be fully understood with collaborative research.
Lessons Learned
The resolution of this scientific puzzle offers several key lessons:
- Vaccine Transparency and Monitoring: Continuous monitoring of vaccine safety is essential, even after approval.
- Rapid Scientific Collaboration: International coordination allowed researchers to share data and identify the underlying mechanism quickly.
- Balancing Risk and Benefit: Public health authorities effectively communicated that, despite rare adverse events, the overall benefits of vaccination in preventing COVID-19 far outweigh the risks.
- Advancing Immunology Knowledge: The findings improve understanding of how immune systems interact with vaccines, paving the way for safer and more effective vaccines in the future.
The identification of the cause of rare vaccine-induced blood clots marks a major scientific achievement. For the public, it provides reassurance that vaccine safety is continuously monitored and that adverse events are investigated thoroughly.
For scientists and clinicians, it represents a breakthrough in understanding how certain immune reactions can lead to serious but extremely rare side effects. More importantly, it equips the global medical community with knowledge to improve vaccine design, safeguard patients, and enhance public confidence in vaccination campaigns.
While VITT remains extremely rare, this research underscores the dedication and rigor of the scientific process: no mystery is too complex when science, collaboration, and careful observation converge. COVID-19 vaccines remain a cornerstone of public health, and this discovery only strengthens the global effort to protect millions from severe disease and death.










Leave a comment