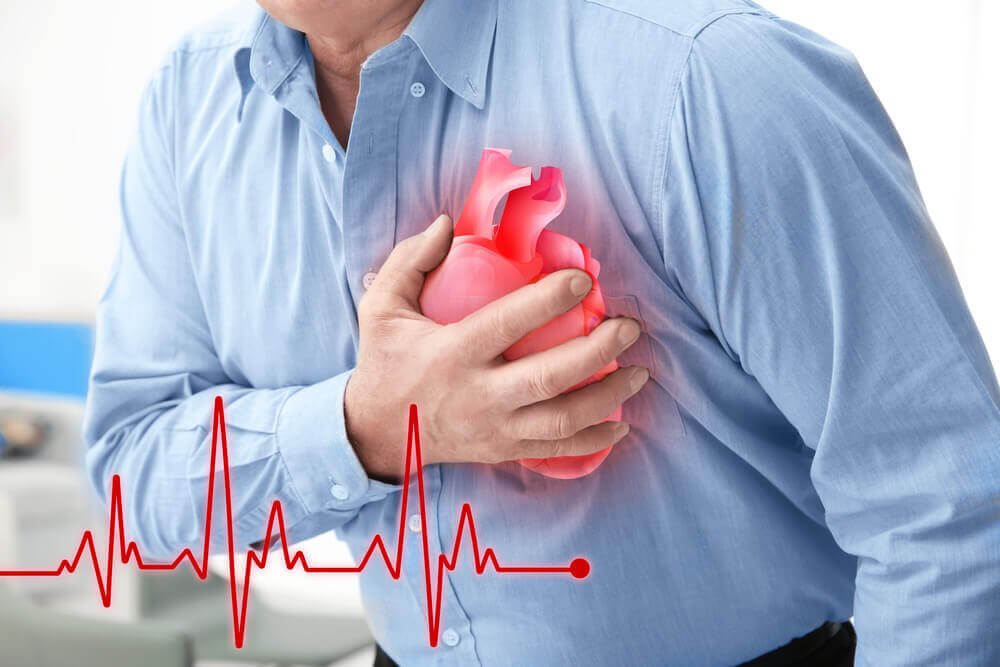
Understanding heart disease is vital as it is a grave issue. It happens when the heart can’t cater to the body’s blood requirements. Men and women can experience it, but men tend to succumb to it earlier. Hence, knowing its symptoms can help in early diagnosis and treatment.
- Discomfort in the Chest: The first and foremost signal suggesting an imminent heart attack is chest discomfort. The feeling is not confined to the chest alone; it can spread to arms, back, neck or jaw, resembling pressure or a feeling of tightness.
- Breathing Difficulties: Experiencing shortness of breath especially when exerting physically could potentially refer to heart disease. Men may also have a persistent cough producing pink or white phlegm tinged with blood, or can experience wheezing.
- Tiredness: Fatigue more than usual, regardless of the level of exertion, also signals heart disease. Continuous low energy conditions can hamper daily life activities and overall life quality.
- Unusual Swelling: Unexpected swelling in legs, feet, abdomen, or ankles could indicate fluid retention, a typical sign of heart diseases. Men may observe sudden weight increase or bloating because of fluid piling up in the body.
- Fluctuating Heartbeat: An irregular, quick heartbeat, or experiencing heart palpitations, meaning feeling your heart pounding, can reveal an underlying heart condition. Any male with this need immediate medical help to rule out probable heart complications.
Certain factors make men more prone to heart disease, such as a sedentary lifestyle, heavy smoking, diabetes, high blood pressure, obesity, and previous heart conditions. Men with a family history of heart complications are at an even higher risk.
Heart Failure: Importance of Early Detection
Early detection is invaluable in heart disease management, helping to mitigate risks like strokes and heart attacks. Men should not dismiss these signs and should immediately seek medical advice if they exhibit any heart disease symptoms. Quick diagnosis and treatment significantly impact the quality of life for heart disease patients.
In conjunction with medical intervention, certain lifestyle modifications can reduce the risk of heart diseases. These include consuming a diet low in cholesterol and saturated fats, regular exercising, stress management, refraining from tobacco and excessive alcohol, and closely monitoring blood pressure and cholesterol levels.