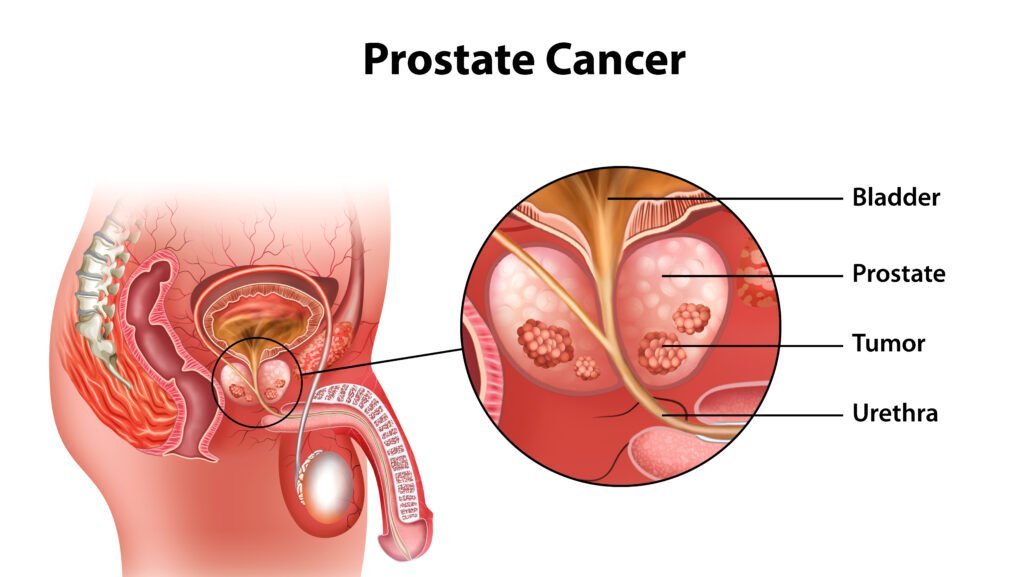
Prostate cancer threat is skyrocketing at an alarming rate in India, with expectations to drastically increase by 2040 as per a study by Lancet. This distressing forecast has sparked critical concerns amongst health experts and policy-making bodies, underscoring the urgency of raising public wakefulness and active prevention methods to tackle this fatal health issue. Grasping the risk components associated with prostate cancer becomes vital in dealing with this emerging health challenge.
Age And Gender
The primary risk component for prostate cancer is age, with the majority of diagnoses occurring in males above 50 years old. The threat of prostate cancer significantly amplifies with advancing age. Early detection and routine screenings are absolutely crucial in managing this disease effectively.
Family History of Cancer
A family history with prostate cancer can considerably raise an individual’s chances of being diagnosed with the disease. Genetics play an important role in making certain individuals prone to prostate cancer. Awareness of one’s genealogical history and genetic vulnerability aids in risk evaluation and necessary precautionary steps.
Poor Lifestyle Choices Can Trigger Prostate Cancer
Unhealthy lifestyle practices, including poor nutrition, physical inactivity, and smoking, can increase the risk of prostate cancer. Incorporating a wholesome diet with a generous proportion of fruits, veggies, and grains, along with regular physical exercise, can help fend off prostate cancer. Shunning tobacco and maintaining appropriate weight are also key elements in protecting prostate health.
Geographic Factors
Research has found racial and geographical factors to have an impact on prostate cancer risk. For instance, African American males display higher occurrence rates of prostate cancer in comparison to men of other races. Further, people residing in regions with high environmental risk components may experience a higher likelihood of getting the disease.
Hormonal Discrepancy and Obesity
High levels of testosterone, a hormonal imbalance, have been linked to an increased prostate cancer risk. Obesity is another significant contributor to the disease, as additional body fat can result in inflammation and hormonal variations that induce cancer development. Balancing hormone health and maintaining an ideal weight are critical in lowering prostate cancer risk.
The Lancet Report has recently issued an alarming projection regarding Prostate Cancer becoming a rapidly growing concern in India by 2040. This study, a wake-up call to the world, emphasizes the urgency of addressing the looming healthcare crisis. Stay informed and stay safe!