New Delhi, 15 August 2025: Abdominal pain can be alarming—especially when it strikes without warning. For many, this pain may stem from either kidney stones or gallbladder stones—two different yet often confused conditions. Although both involve the formation of stones inside the body, they originate in completely different organs and present distinct symptoms.
Knowing the difference between the two conditions at home can help you make informed decisions and seek the right medical help when needed. This article breaks down everything you need to know—from causes and symptoms to how you can tell them apart on your own.
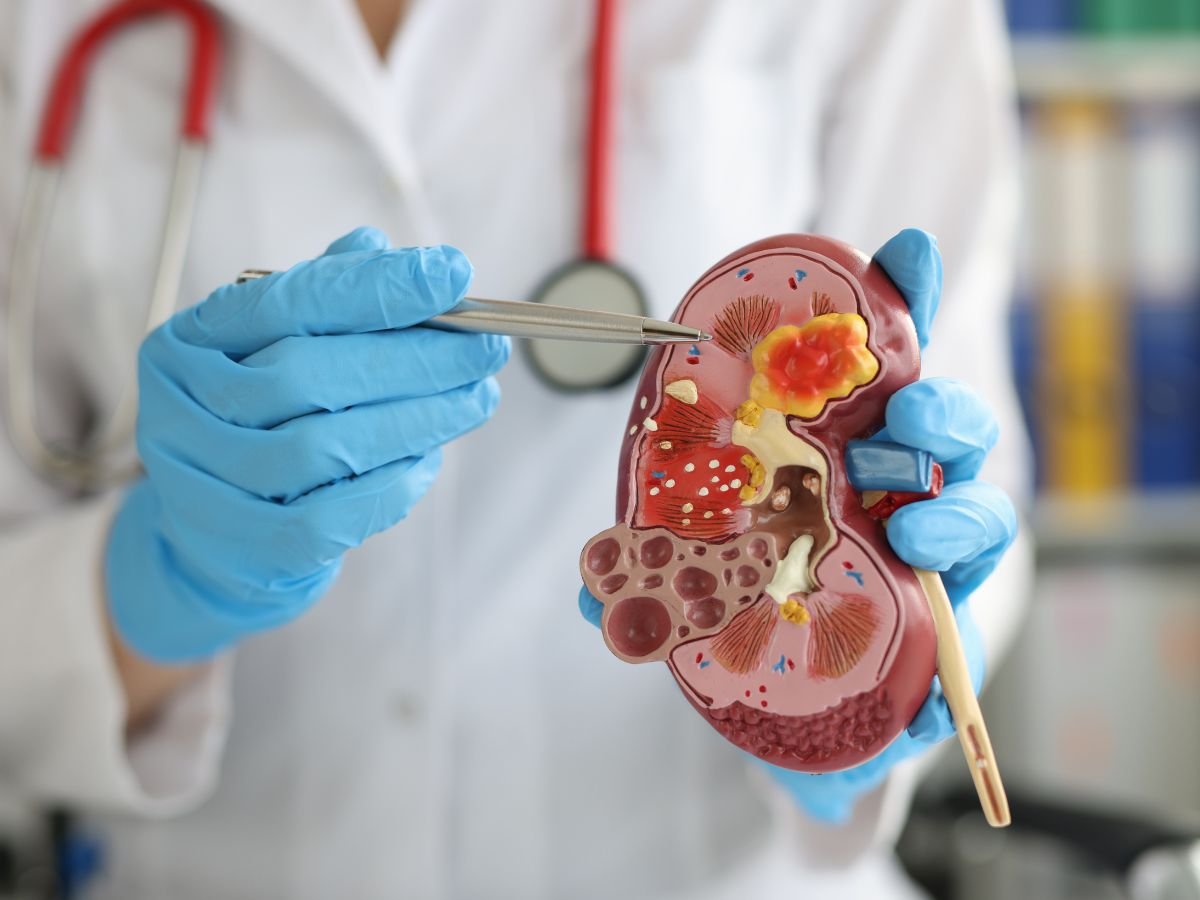
What Are Kidney Stones?
Kidney stones are hard deposits made of minerals and salts that form inside the kidneys. These form when urine becomes concentrated, allowing minerals like calcium, oxalate, and uric acid to crystallize and stick together. Common risk factors include:
- Dehydration
- High intake of sodium or animal protein
- Family history of kidney stones
- Certain medications and medical conditions
What Are Gallbladder Stones (Gallstones)?
Gallstones develop in the gallbladder, a small organ located beneath the liver. The gallbladder stores bile, which helps in digesting fats. When bile contains too much cholesterol or bilirubin—or doesn’t empty properly—stones can form. Risk factors include:
- Obesity or rapid weight loss
- Poor diet (high in fat or cholesterol)
- Hormonal changes (especially in women)
- Family history of gallstones
Key Differences Between Kidney and Gallbladder Stones
| Feature | Kidney Stones | Gallstones |
|---|---|---|
| Location | Form in the kidneys or urinary tract | Form in the gallbladder |
| Main Cause | Concentrated urine, high minerals | Imbalance in bile composition |
| Common Pain Area | Side, lower back, or groin | Right upper abdomen or under the ribs |
| Pain Character | Sharp, sudden, wave-like pain | Dull, constant pain (especially after fatty meals) |
| Urine Changes | Blood in urine, pain while urinating | Dark urine (when bile ducts are blocked) |
| Other Symptoms | Nausea, vomiting, frequent urination | Nausea, vomiting, bloating, jaundice |
Symptoms of Kidney Stones You Can Recognize at Home
- Sharp, intense flank or lower back pain
- Pain usually starts suddenly and can radiate toward the groin.
- Blood in urine
- Urine may appear pink, red, or brown.
- Frequent or painful urination
- Especially when the stone is moving through the urinary tract.
- Nausea and vomiting
- Can occur due to severe pain or blockage.
- Difficulty sitting or lying comfortably
- Pain may make it hard to find a comfortable position.
Symptoms of Gallbladder Stones You Can Recognize at Home
- Upper right abdominal pain
- Often triggered by eating fatty foods.
- Pain that radiates to the right shoulder or back
- Can be constant or last a few hours.
- Indigestion, nausea, and bloating
- Especially after meals.
- Jaundice
- Yellowing of the skin or eyes if the bile duct is blocked.
- Dark-colored urine and pale stools
- Occur when bile flow is obstructed.
When and Why You Should Know the Difference
While both conditions cause discomfort, their treatments differ significantly.
- Kidney stones may pass naturally with increased fluid intake and pain medication. However, larger stones may require procedures such as lithotripsy or surgical removal.
- Gallstones, on the other hand, may require gallbladder removal surgery (cholecystectomy) if they cause frequent attacks or complications like gallbladder inflammation or pancreatitis.
Identifying the right condition early helps avoid complications, like kidney damage or gallbladder infection.
How to Differentiate at Home: A Quick Self-Check
Ask yourself the following:
- Is your pain sharp and shifting from the back to groin? It’s likely kidney stones.
- Does your pain come after eating fried or fatty meals and stay in the upper right abdomen? Think gallstones.
- Are you noticing blood in urine or burning while urinating? These are classic signs of kidney stones.
- Do you feel bloated, nauseated, or yellow in the eyes/skin? This could point to gallstones.
- Are your stools pale and urine dark? That’s often a sign of bile duct obstruction from gallstones.
Causes and Prevention Tips
Kidney Stones:
- Causes: Low fluid intake, high salt/protein diet, obesity, genetic factors
- Prevention:
- Drink at least 2-3 liters of water daily
- Reduce sodium intake
- Eat calcium-rich foods (avoid supplements without guidance)
- Limit animal protein and oxalate-rich foods (spinach, chocolate, nuts)
Gallbladder Stones:
- Causes: High cholesterol, sluggish bile movement, hormonal shifts
- Prevention:
- Maintain a healthy weight
- Avoid rapid dieting or fasting
- Limit high-fat, greasy, and processed foods
- Include more fiber-rich foods like fruits and vegetables
Treatment Options
Kidney Stones:
- Hydration therapy: Drinking fluids to help pass small stones
- Pain management: Over-the-counter painkillers like ibuprofen
- Medical procedures:
- Shockwave lithotripsy to break stones
- Ureteroscopy or percutaneous nephrolithotomy for removal
Gallstones:
- Lifestyle changes: Low-fat diet, weight management
- Medications: To dissolve small cholesterol stones (takes months)
- Surgery:
- Laparoscopic cholecystectomy (common)
- Removal of the gallbladder usually does not impact digestion significantly
When to See a Doctor
You should seek medical help if you:
- Experience extreme abdominal pain that doesn’t improve
- Have fever, chills, or signs of infection
- Notice blood in urine or have trouble urinating
- Show signs of jaundice
- Have persistent vomiting, dehydration, or confusion
Kidney stones and gallbladder stones can both cause intense discomfort, but their origins, symptoms, and treatment are entirely different. By observing pain location, digestion patterns, urine/stool changes, and timing, you can often tell the difference at home.
That said, no home diagnosis should replace professional medical advice. If symptoms persist or worsen, it’s always best to consult a healthcare provider for accurate testing and timely treatment.