New Delhi, 01 June 2025: High cholesterol is often referred to as a “silent killer” because it shows no obvious symptoms yet plays a dangerous role in the development of heart disease and sudden cardiac arrest. Despite growing awareness, millions of people worldwide continue to live with unhealthy cholesterol levels, unknowingly putting their hearts at serious risk. In this article, we explain exactly how high cholesterol impacts your cardiovascular system, increases your chances of cardiac arrest, and what steps you can take to manage it effectively.
What is Cholesterol?
Cholesterol is a waxy, fat-like substance found in your blood. Your body needs it to build healthy cells, produce hormones, and aid in digestion. However, when cholesterol levels rise too high—especially low-density lipoprotein (LDL) cholesterol, often called “bad cholesterol”—it can have harmful effects.
There are two main types of cholesterol:
- LDL (Low-Density Lipoprotein): Referred to as “bad” cholesterol, high levels of LDL can lead to plaque buildup in arteries.
- HDL (High-Density Lipoprotein): Known as “good” cholesterol, HDL helps remove excess cholesterol from your bloodstream.
How High Cholesterol Affects Your Heart
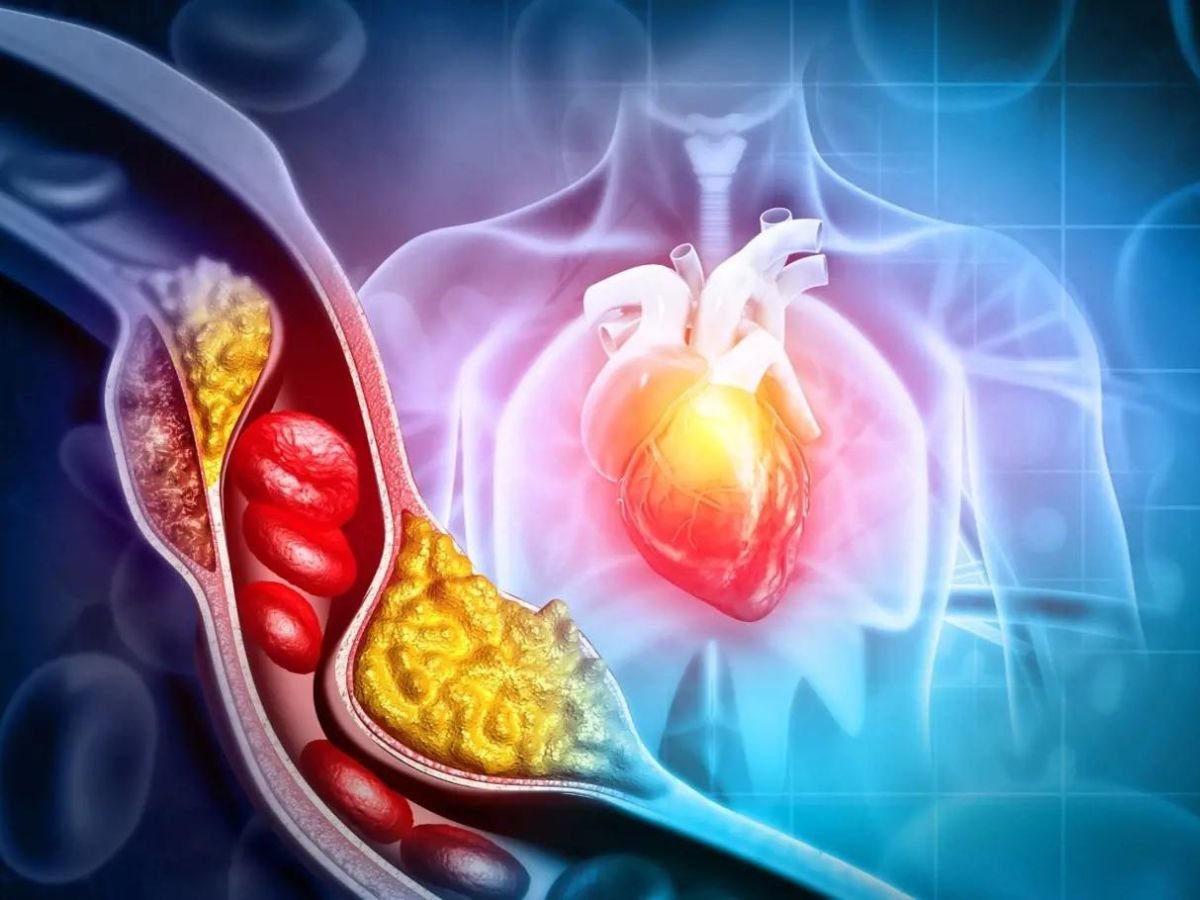
When there is too much LDL cholesterol in your blood, it starts to deposit along the walls of your arteries. Over time, this leads to atherosclerosis, a condition where arteries become hardened and narrowed due to plaque buildup. Here’s how this impacts your heart:
1. Restricted Blood Flow
As the plaque builds up, it reduces or completely blocks the flow of oxygen-rich blood to your heart muscle. This forces the heart to work harder, leading to elevated blood pressure and increased strain on the cardiovascular system.
2. Risk of Blood Clots
Plaques in arteries can rupture, triggering the formation of a blood clot. If the clot blocks a coronary artery, it can cut off the heart’s oxygen supply—resulting in a heart attack. If the blockage affects arteries in the brain, it can cause a stroke.
3. Coronary Artery Disease (CAD)
One of the most common consequences of high cholesterol is coronary artery disease, a condition that can lead to chest pain (angina), shortness of breath, and ultimately, heart failure if not managed.
4. Cardiac Arrest
Cardiac arrest is a sudden loss of heart function. While it’s often triggered by an electrical malfunction in the heart, high cholesterol significantly raises the risk. That’s because restricted blood flow and damaged arteries disrupt the heart’s normal rhythm and oxygen supply.
Key Warning Signs of High Cholesterol
High cholesterol itself doesn’t cause symptoms, but its consequences do. Watch for warning signs that may indicate your cholesterol is affecting your heart:
- Chest pain or tightness
- Shortness of breath
- Fatigue
- Dizziness or lightheadedness
- Palpitations
- Numbness or coldness in extremities (due to poor circulation)
If you are experiencing any of these symptoms, especially with a family history of heart disease, consult your doctor immediately.
What Causes High Cholesterol?
Several factors contribute to high cholesterol levels, including:
- Unhealthy diet (high in saturated fats and trans fats)
- Lack of physical activity
- Smoking
- Obesity
- Diabetes
- Genetics (familial hypercholesterolemia)
Even people who are thin or physically active can have high cholesterol if it runs in the family.
How to Manage and Lower High Cholesterol
Managing cholesterol isn’t just about taking medication—it’s about making holistic lifestyle changes. Here’s what experts recommend:
1. Eat Heart-Healthy Foods
Opt for foods that are rich in soluble fiber, omega-3 fatty acids, and plant sterols, such as:
- Oats, beans, lentils
- Fatty fish like salmon and sardines
- Nuts like almonds and walnuts
- Olive oil and avocados
- Fresh fruits and leafy greens
2. Avoid Trans Fats and Saturated Fats
Reduce your intake of:
- Red meat
- Full-fat dairy products
- Packaged snacks and fast food
- Fried foods
These foods are known to raise LDL cholesterol levels.
3. Exercise Regularly
Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate activity 5 times a week. Brisk walking, swimming, and cycling are great heart-healthy exercises that also help raise HDL (good) cholesterol.
4. Quit Smoking
Smoking lowers good cholesterol and damages your blood vessels. Quitting helps improve your HDL levels and overall heart health.
5. Limit Alcohol Consumption
Drinking too much alcohol can raise your cholesterol and blood pressure. If you drink, do so in moderation—1 drink per day for women, 2 for men.
6. Take Medication If Prescribed
If lifestyle changes aren’t enough, your doctor may prescribe statins or other medications to help lower your LDL levels and reduce the risk of heart complications.
Since high cholesterol has no symptoms, regular blood tests are crucial. Adults over 20 should get their cholesterol levels checked at least once every 4 to 6 years. People with risk factors may need more frequent testing.
High cholesterol is a serious but manageable risk factor for heart disease and cardiac arrest. The key is early detection and a proactive approach to health. Don’t wait for a heart attack to serve as a wake-up call—start managing your cholesterol today by adopting healthier habits, eating a balanced diet, and getting regular check-ups.