A dangerous strain of mpox, once limited to the Democratic Republic of Congo, is now spreading quickly across Kenya and other African countries. This has caused significant concern among health authorities.
The Spread of Mpox
The World Health Organization (WHO) has confirmed that this new strain is a major health threat. In Kenya, a truck driver traveling to Uganda, Rwanda, and Tanzania was found to be infected with this strain on July 29, according to the Ministry of Health.
The Africa Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (Africa CDC) reported that the disease has been found in 10 African countries this year. For the first time, Burundi and Rwanda have reported cases of mpox.
What is Mpox?
Mpox is a zoonotic disease, meaning it can spread from animals to humans. It is caused by the Monkeypox virus, which is related to the virus that causes smallpox. The disease can spread through direct contact with an infected person or animal, their body fluids, or during physical contact like kissing, cuddling, or sex.
According to the CDC, the virus can enter the body through broken skin, the respiratory tract, or the eyes, nose, or mouth.
Alarming Statistics
A report from The Sun revealed that 130 children and teenagers in refugee camps in the Democratic Republic of Congo (DRC) have been infected with this highly contagious new mpox strain.
This strain, known as clade I, causes more severe illness than the clade II virus that led to a global outbreak in 2022. The fatality rate for clade I is around five percent in adults and 10 percent in children, while clade II had a fatality rate of three percent.
According to DailyStar.co.uk, this strain, called clade 1b, spreads more easily between people and has mutations not detected by current tests.
Symptoms of Mpox
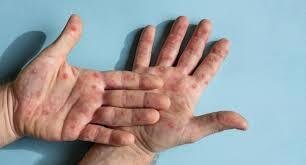
The initial symptoms of mpox include fever, chills, headache, muscle aches, and swollen lymph nodes. After a few days, a rash develops on the face and then spreads to other parts of the body. The rash can resemble chickenpox or syphilis, and scabs form and eventually fall off.
The incubation period, or the time from exposure to the first symptoms, is typically between 6-13 days but can range from 5-21 days.
Precautions and Isolation
People who have recently traveled and show symptoms should isolate themselves at home or in a hospital to prevent spreading the infection. The CDC recommends an isolation period of about three weeks, until all scabs have fallen off.
Preventive Measures
Here are some steps to avoid getting mpox:
Avoid Skin Contact: Stay away from people who are infected or have a rash that may be mpox.
Hand Hygiene: Wash hands thoroughly with soap and water or use an alcohol-based sanitizer.
Cough and Sneeze Etiquette: Cover your mouth and nose with your arm when coughing or sneezing.
Safe Sex Practices: Avoid unprotected sex with anyone suspected of having mpox.
By following these precautions, you can help prevent the spread of mpox and protect yourself and others from this serious disease.